Deeper dive into Navigating
Logistics
- Projects
Review
- Consists of a grid of “costs” (costmap) and a coordinate system
- Map server “publishes” the map on the /map topic
SLAM
- An algorithm that builds up a map while collecting sensor and analyzing it statistically
- The map as it is being built is published by the map_server
- You can save the map to a file so that it remembers it to the next run
Navigation
- AMCL: Given lidar sensor data and a map, estimates the true location of the robot
- Calculation is reset when amcl receives a new pose_estimate
- This estimate is different from /odom (why?)
- AMCL publishes a /tf transform between /map and /odom (note this is the “highest probability” location)
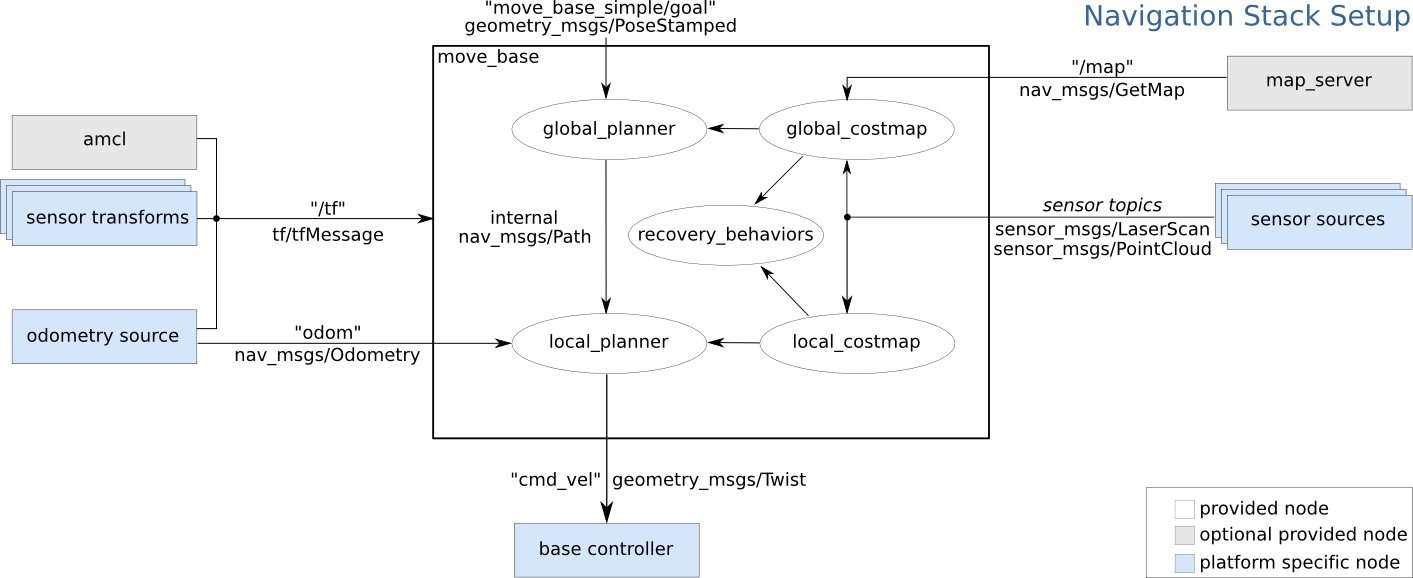
move_base
- A sophisticated, pluggable architecture
- Allows for new algorithms to be designed and tested
- Parameterized for configuration
- Uses ROS “actions” to initiate, monitor, and report success
- Initial goal is: /MoveBaseActionGoal
- 5: Actions
Components of move_base
- Global Planner: Creates a plan from the current position (AMCL) to the goal position with respect to a map. May use any of a number of algorithms (including A*)
- Local Planner: Given the local map (built in real time from sensors), considers location and velocity and computes the near part of the plan.
- costmap-2d: General package to build, maintain, update and access a multi-layer 2d map. Used for both local and global maps and for other things
- Recovery behaviors: either map clearing or rotation recovery heuristics used when robot appears to be stuck.
FLows
How move_base works - global planner
- Uses base_global planner to comnpute a path from current position to goal
- This plan is with respect to the global costmap (from /map topic and
map_server) - Look at ROS global planner for visuals
- Interesting parameters:
/use_dijkstra (bool, default: true) # If true, use dijkstra's algorithm. Otherwise, A*.
/use_quadratic (bool, default: true) # If true, use the quadratic approximation of the potential. Otherwise, use a simpler calculation.
/use_grid_path (bool, default: false) # If true, create a path that follows the grid boundaries. Otherwise, use a gradient descent method.
How move_base works - local planner
- Create a local map grid from the local costmap) with costs representing distances to the final goal
- Uses base_local_planner to determine the next motion in the immediate future
The two book chapters
Topics for further study
- The SLAM Toolbox
- The Python Robotics Pacakge
 (random Image from picsum.photos)
(random Image from picsum.photos)