Reminder: Readings are your responsibility. You will be expected to come to class prepared, having read the material, and ready to participate in the discussion
Logistics
Factors in Assessment of Projects
- The number of students on the team and ambition of the project
- Expectation is based on the number of people and the available time
- 5-6 weeks @ around 5-10 hrs per week per student
- Quality: Does the project work on repeated runs (not just once)
- Communication: How well explained is the project in the deliverable
Standups
- Thank you for submitting
- Reread the instructions!
- Simple set of bullets, not a whole project plan
Lab
- Link to Lab coverage hours
- Link to Report Robot Problems
- Are you able to use the lab
- What additional time slots do you need?
- Remember:
sudo shutdown now (onboard), power switch off, unplug battery.
ROBB is working again. Remember to report robot problems so we can track them and fix them
Review of Fiducials PA
Path Planning
- For now, just focus on a mobile robot like a car
- Goal of path planning: get the robot from where it is to a destination
- Beyond that there are many variations
- What kind of map is present?
- Are the obstacles encountered known ahead of time, and can they move?
Types of maps - Graphs
- Define places where Robot can be (nodes)
- Define which ones are connected (edges)
- Edge information includes
- What path to take
- What the “cost” would be of taking that path (surface, distance, desirability)
- Planning the route becomes a graph searching problem
- Find the “cheapest” path between two nodes
Types of maps - Occupancy Grids
- Divide the “area” into a regular grid
- Indicate whether each “cell” in a grid is occupied or free
- Occupancy Grids can be multi-layer
- For example to indicate
- access for different types of vehicles
- areas that are free but discouraged
- Treat each cell in the grid as a
node with 4 or 8 edges
Behind the scenes
- amcl subscribes to a topic
geometry_msgs/PoseWith
- rviz command 2d pose estimate publishes the new proposed pose on that topic
- When amcl receives that message it resets its collection of candidate poses
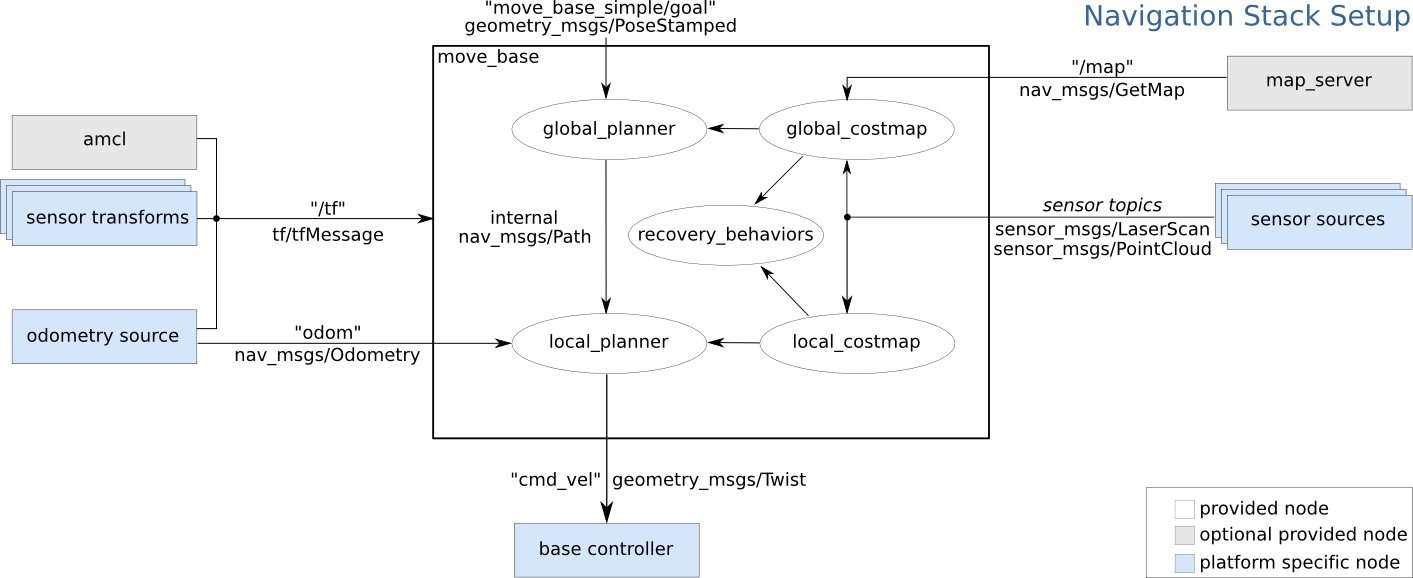
Going inside the Nav Stack
- Global planner: works out best path assuming map is accurate
- global costmap: How safe or unsafe is each spot on the map
- Published on /move_base/global_costmap/costmap
- Planner view shows what the planned path to the nav goal is
- Local Planner:
- Adjusts the global plan based on newly detected obstacles
- Map shows square area around robot with further analysis
1 Color shows safe areas in cold colors (like blue) and dangerous areas in warm colors (like red)
Navigating in code
- Look at patrol.py
- It is a
SimpleActionClient which sends a repeating sequence of two Action Goals to move_base
- There’s nothing tricky about itself.
- The challenge might be getting all the other bits set up so that it will work correctly
Some more references:
Thank you. Questions? (random Image from picsum.photos)
(random Image from picsum.photos)